CI/CD Integration using Server token
The Server Auth Token allows you to authenticate Zephyr plugins at the organization level without needing individual user credentials for every operation. It identifies the user performing actions via their email and enables secure access to Zephyr on behalf of your organization.
Server tokens provide organization-level authentication. For individual user authentication, see the Personal Token CI/CD Integration guide. Personal tokens are useful for personal projects or when you need user-specific permissions. Learn more in the CI/CD Personal Token guide.
Overview
Generate an Server API Token
To use Zephyr Cloud in CI/CD pipelines, you'll need an API token for authentication:
Organization Settings
Go to your Organization Settings in Zephyr.

Server Tokens section
Navigate to the Server Tokens section.
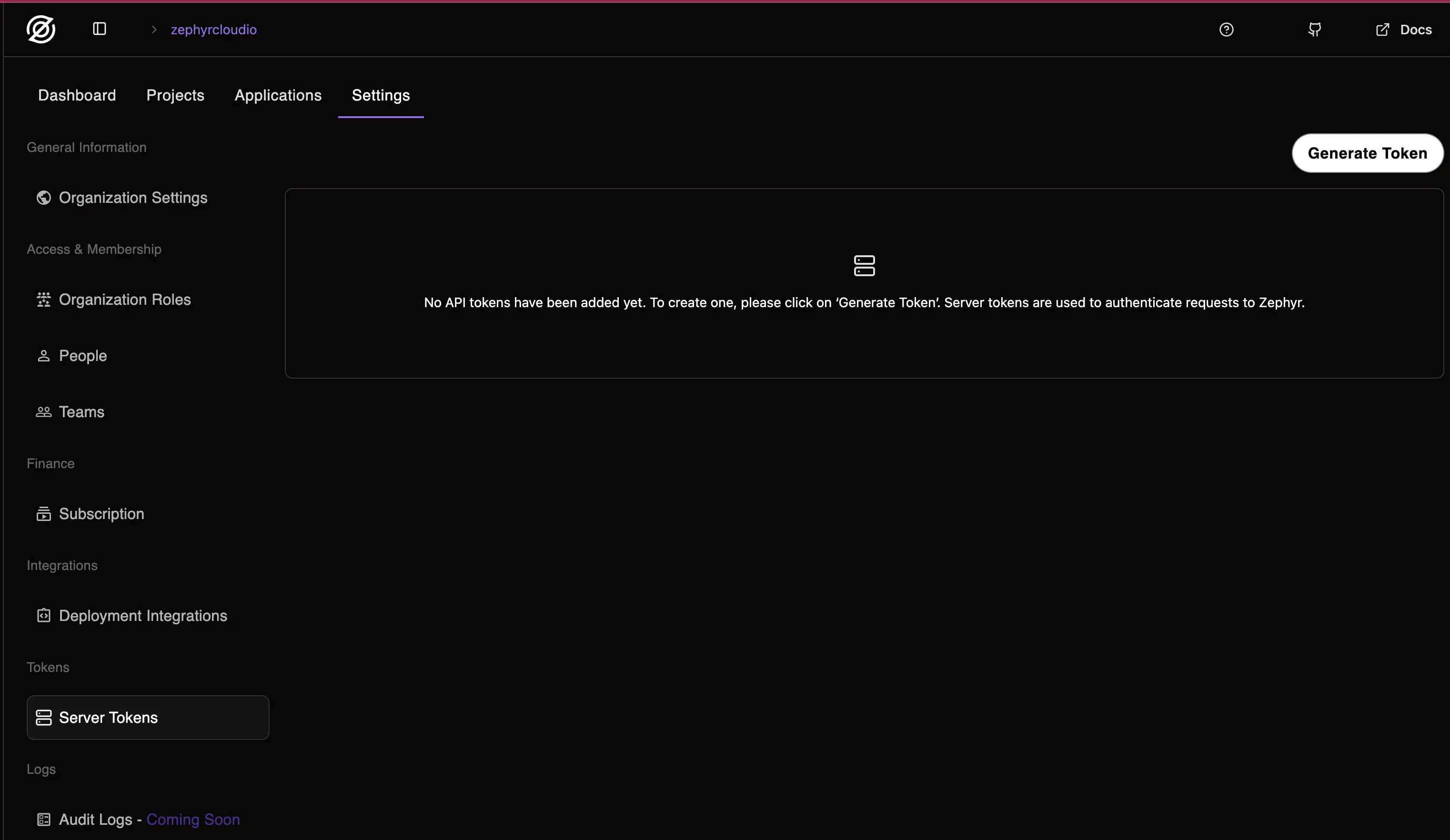
Click Generate Token Button
Fill out the required information about the token you're about to generate
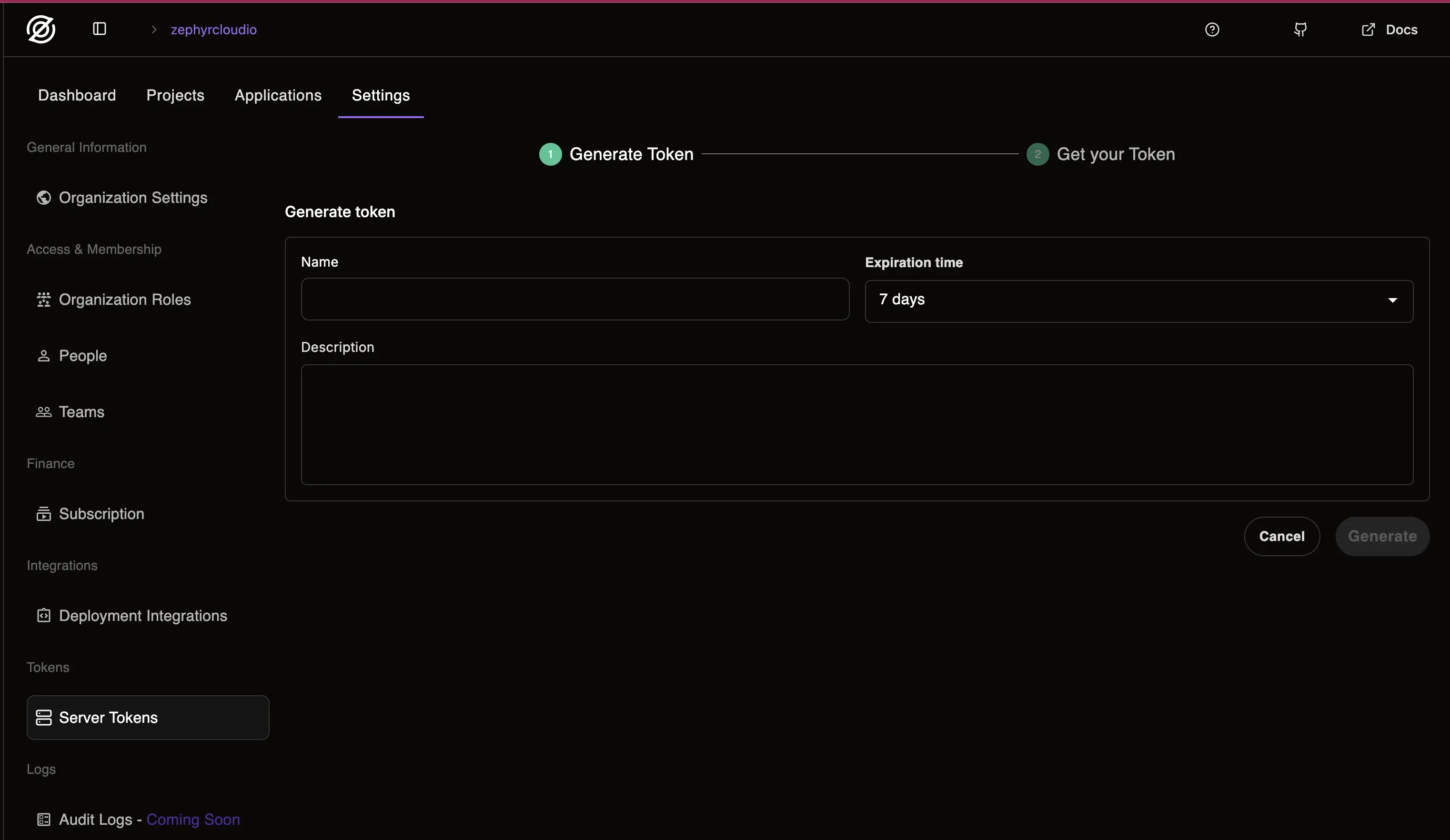
Click Generate
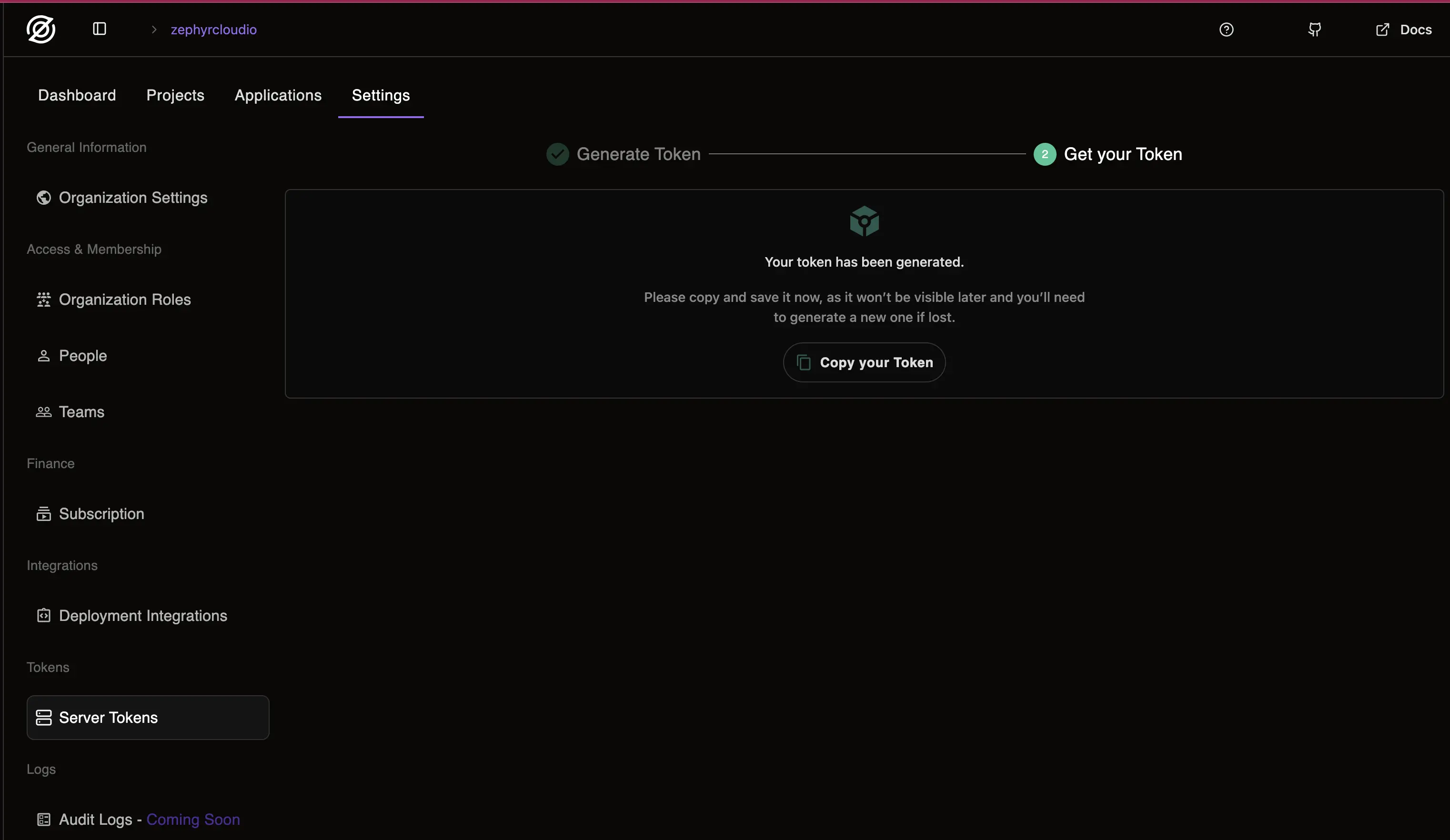
Copy the token for usage where you need to use it
GitHub Actions
Zephyr requires an authenticated user to publish updates. Configure your GitHub Actions pipeline to build and deploy with Zephyr by adding a token to your repository secrets.
Adding the GitHub Secret
- Create a token on your organization settings page
- Add it as a repository secret in GitHub
- The secret must be assigned to the
ZE_SERVER_TOKENenvironment variable - Set user email
Authentication Behavior
When the Zephyr plugin detects the ZE_SERVER_TOKEN environment variable, it will automatically authenticate with the Zephyr API, bypassing the usual login step.
The Zephyr needs a user email to identify who is performing builds. You can provide it in one of two ways:
- Automatically from Git config
- Manually via environment variable
ZE_USER_EMAIL
You'll see this confirmation in the console:
GitLab CI/CD
Configure your GitLab Runner pipeline to build and deploy with Zephyr by adding a token to the CI/CD variables.
Adding the GitLab CI/CD Variable
- Create a full access token on your Organization Server tokens page page
- Add it as a CI/CD variable in your GitLab project:
Steps to add the token:
- Navigate to your GitLab project
- Go to Settings → CI/CD
- Expand the Variables section
- Click Add variable
- Configure the variable:
- Key:
ZE_SERVER_TOKEN - Key:
ZE_USER_EMAIL - Value: Your Zephyr API token
- Type: Variable
- Environment scope: All (or specify specific environments)
- Protect variable: ✅ Check if you want to use it only in protected branches
- Mask variable: ✅ Check to hide the value in job logs
- Key:
Using the Token in GitLab CI/CD
In your .gitlab-ci.yml file, the token will be automatically available as an environment variable:
For more explicit control, you can also reference it directly:
Authentication Behavior
When the Zephyr plugin detects the ZE_SERVER_TOKEN environment variable, it will automatically authenticate with the Zephyr API, bypassing the usual login step.
You'll see this confirmation in the console:
Complete Pipeline Example
Here's a full GitLab CI/CD pipeline configured for Zephyr deployment:
Security Notes
- Do not share server tokens publicly.
- Rotate tokens regularly and revoke any that may be compromised.
- Remember: server tokens provide organization-level access, so they are sensitive credentials.
Troubleshooting
Authentication Issues
Token not found error:
- Verify the variables names are exactly
ZE_SERVER_TOKENandZE_USER_EMAIL - Ensure the variables are available in the environment where your job runs
- Check that the token hasn't expired
GitLab-Specific Issues
Protected variables:
- If using protected variables, ensure your pipeline runs on a protected branch or tag
Masked variables:
- Masked variables won't appear in job logs (recommended for security)
- Temporarily unmask if you need to troubleshoot, then re-mask for production
Variable scope:
- Check that the variable scope matches your pipeline's environment requirements
Related Documentation
- Personal Token CI/CD Integration - User-level authentication for CI/CD
- Automation - Automated workflows and deployment strategies
- Teams & Members - Managing organization access and permissions
- Tags & Environments - Managing deployment targets